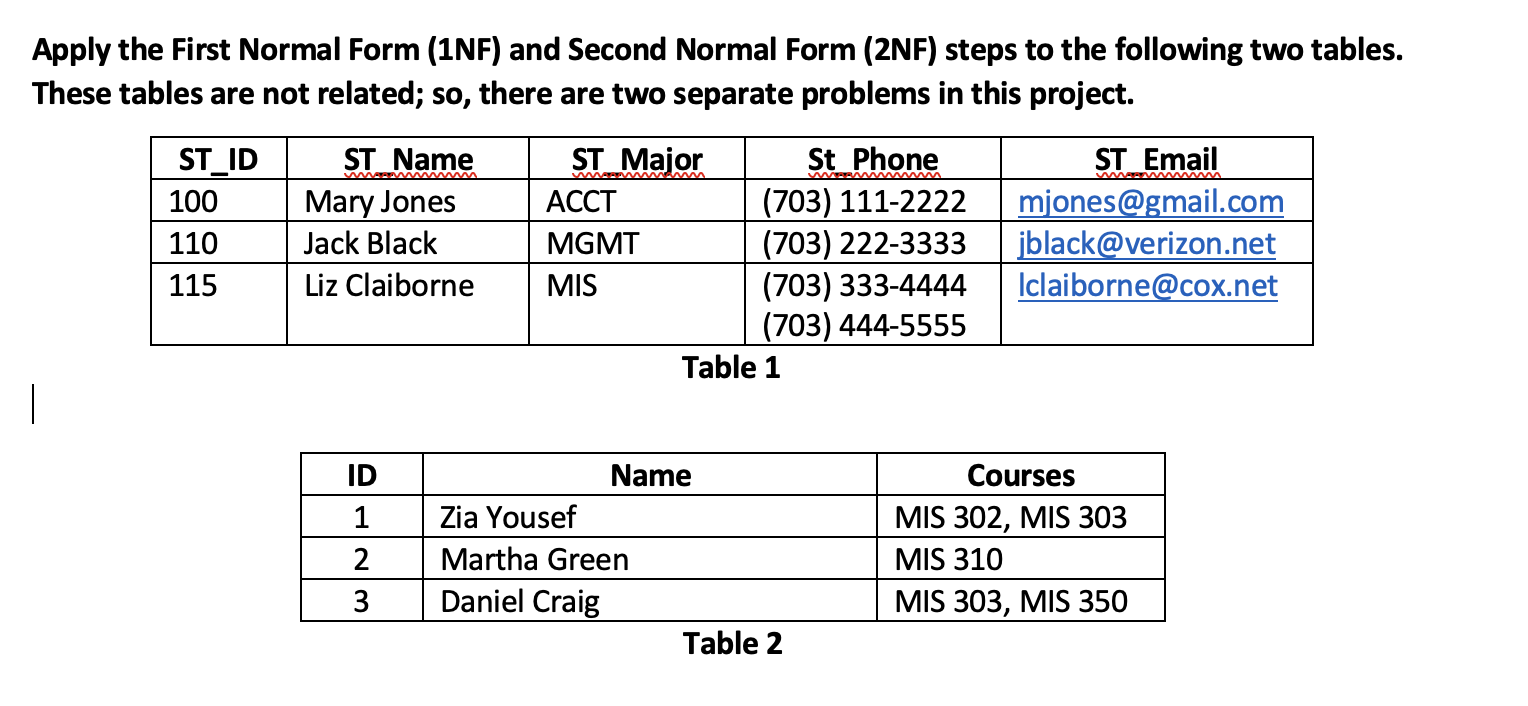
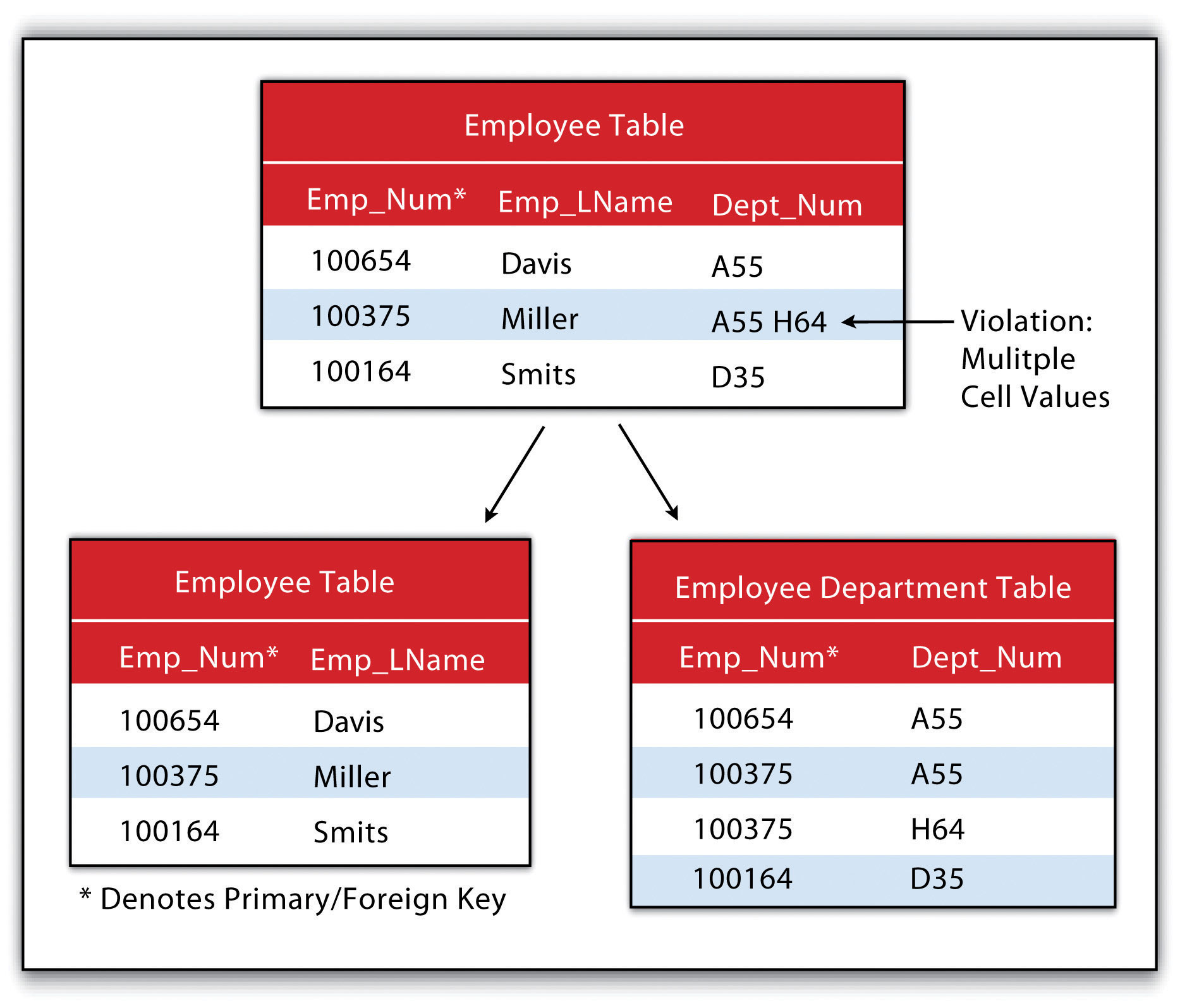
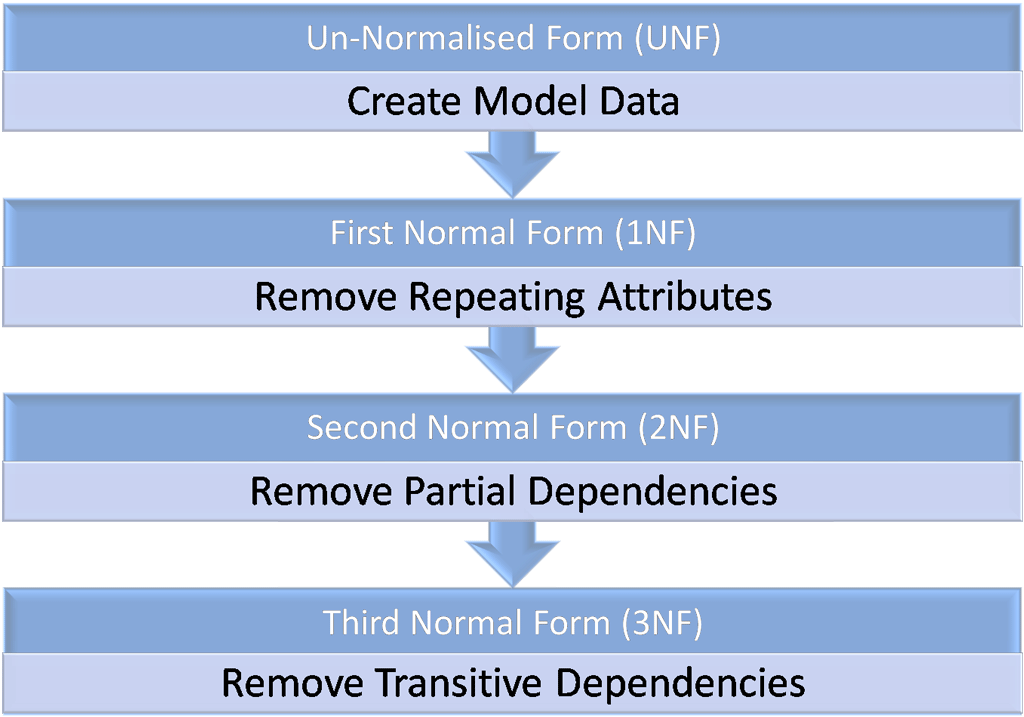
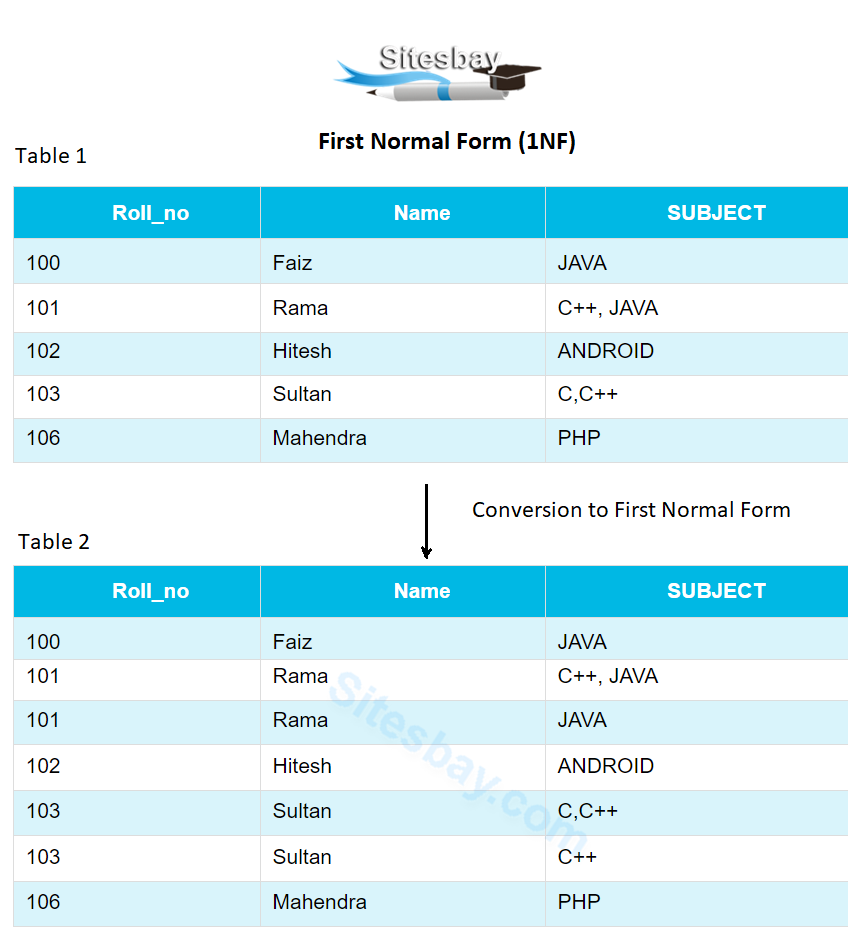
First Normal Form And Second Normal Form
First Normal Form And Second Normal Form - A table, as below, must be. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic. The second normal form (2nf) states that non. The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf.
The second normal form (2nf) states that non. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic. The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. A table, as below, must be.
The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic. The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. The second normal form (2nf) states that non. A table, as below, must be.
PPT Data Normalization PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. A table, as below, must be. The second normal form (2nf) states that non. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic.
AlgoDaily Normalization in SQL
The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. A table, as below, must be. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic. The second normal form (2nf) states that non.
Solved Apply the First Normal Form (1NF) and Second Normal
The second normal form (2nf) states that non. The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. A table, as below, must be. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic.
Second Normal Form (2NF) Database Normalization in Hindi
The second normal form (2nf) states that non. The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. A table, as below, must be. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic.
Fillable Online cs ius edu First Normal Form Second Normal Form Third
The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic. The second normal form (2nf) states that non. A table, as below, must be.
Geospatial Database Management
The second normal form (2nf) states that non. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic. A table, as below, must be. The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf.
Normalization in DBMS Types of Normalization with Examples DatabaseTown
The second normal form (2nf) states that non. The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic. A table, as below, must be.
AlgoDaily Normalization in SQL
The second normal form (2nf) states that non. The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. A table, as below, must be. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic.
Standard Query Language
A table, as below, must be. The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic. The second normal form (2nf) states that non.
The Second Normal Form (2Nf) States That Non.
The first normal form (1nf) states that each attribute in the relation is atomic. The first normal form (1nf), like all normal forms, has specific requirements to be validated as 1nf. A table, as below, must be.