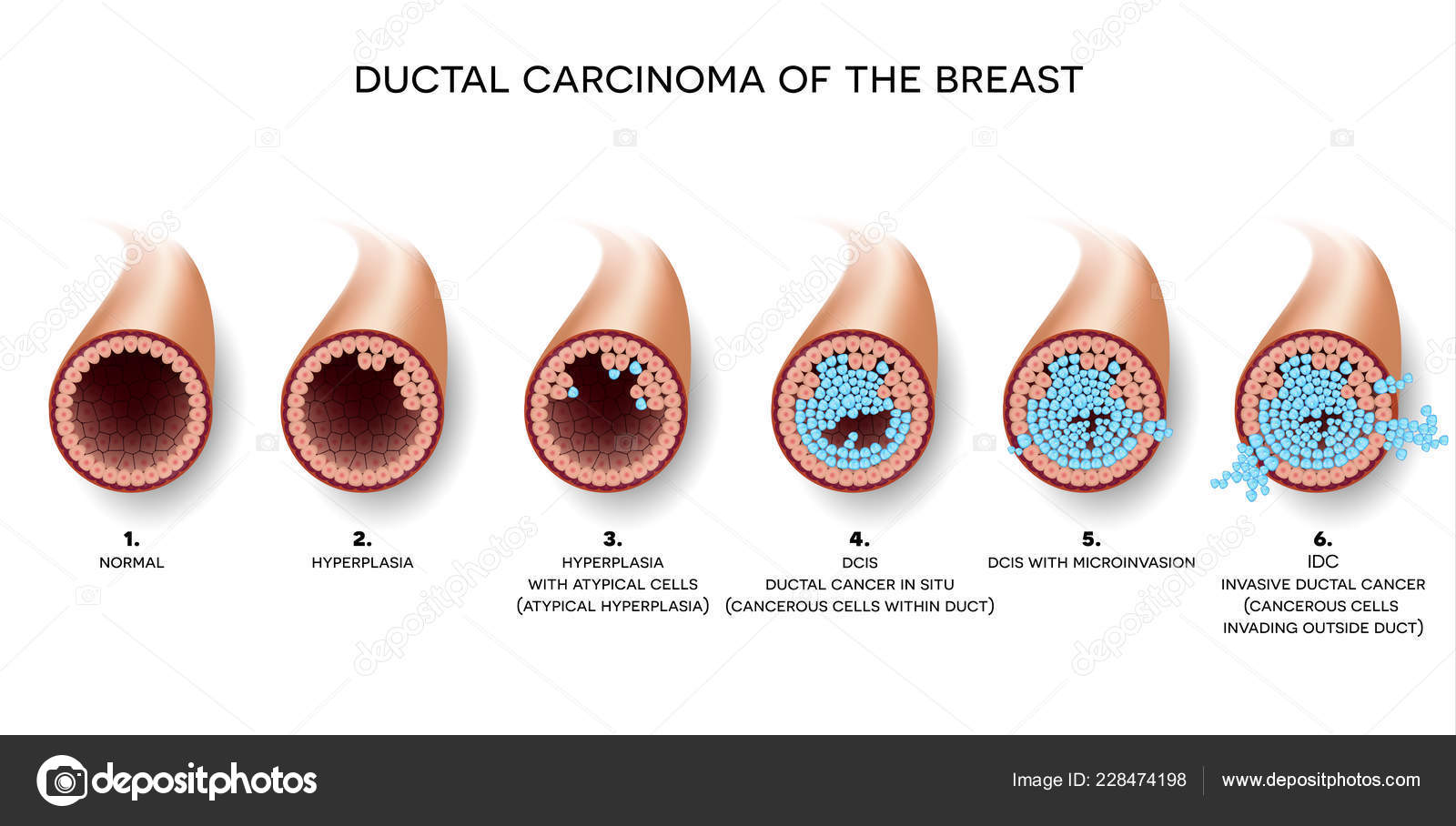
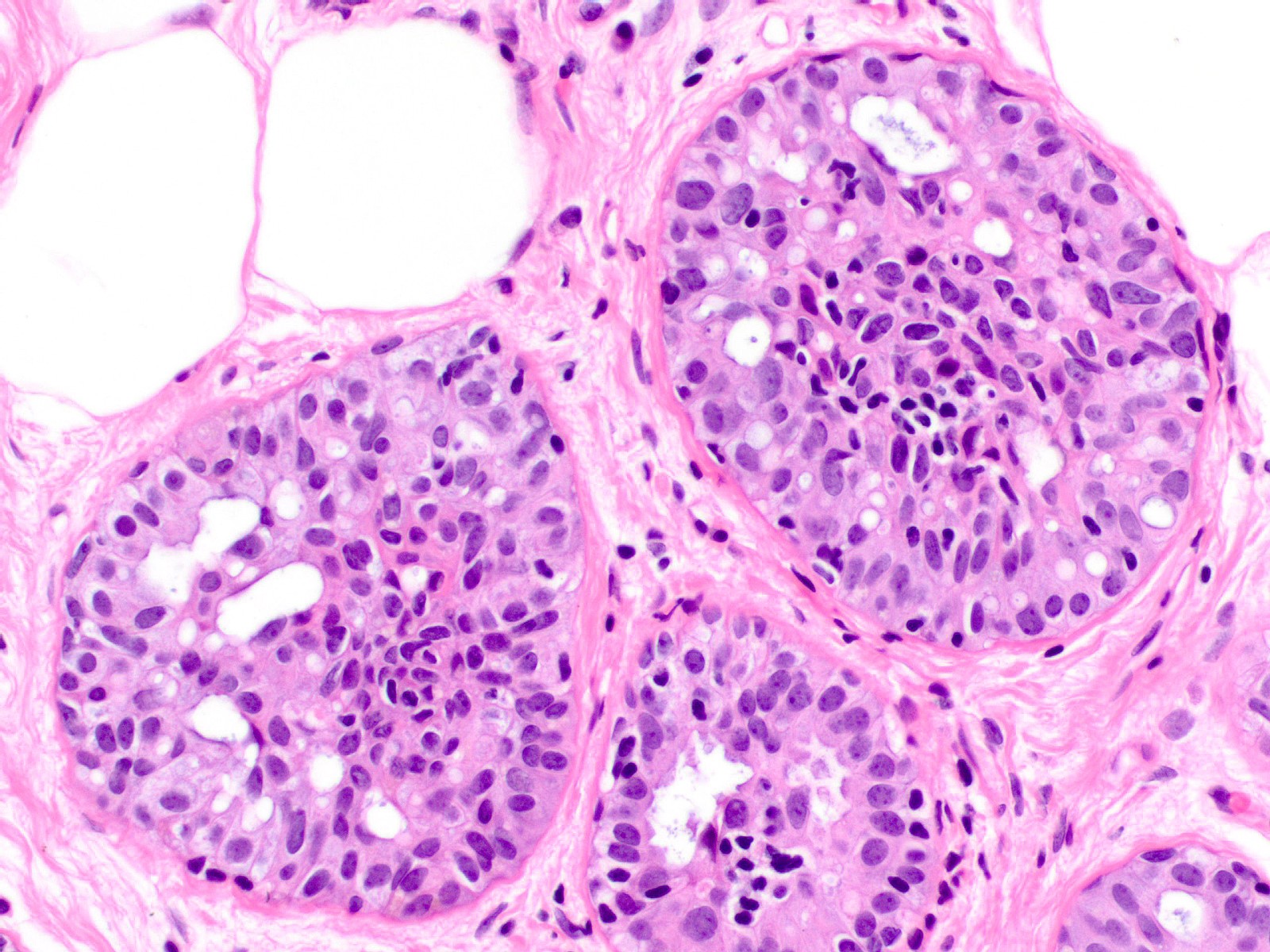
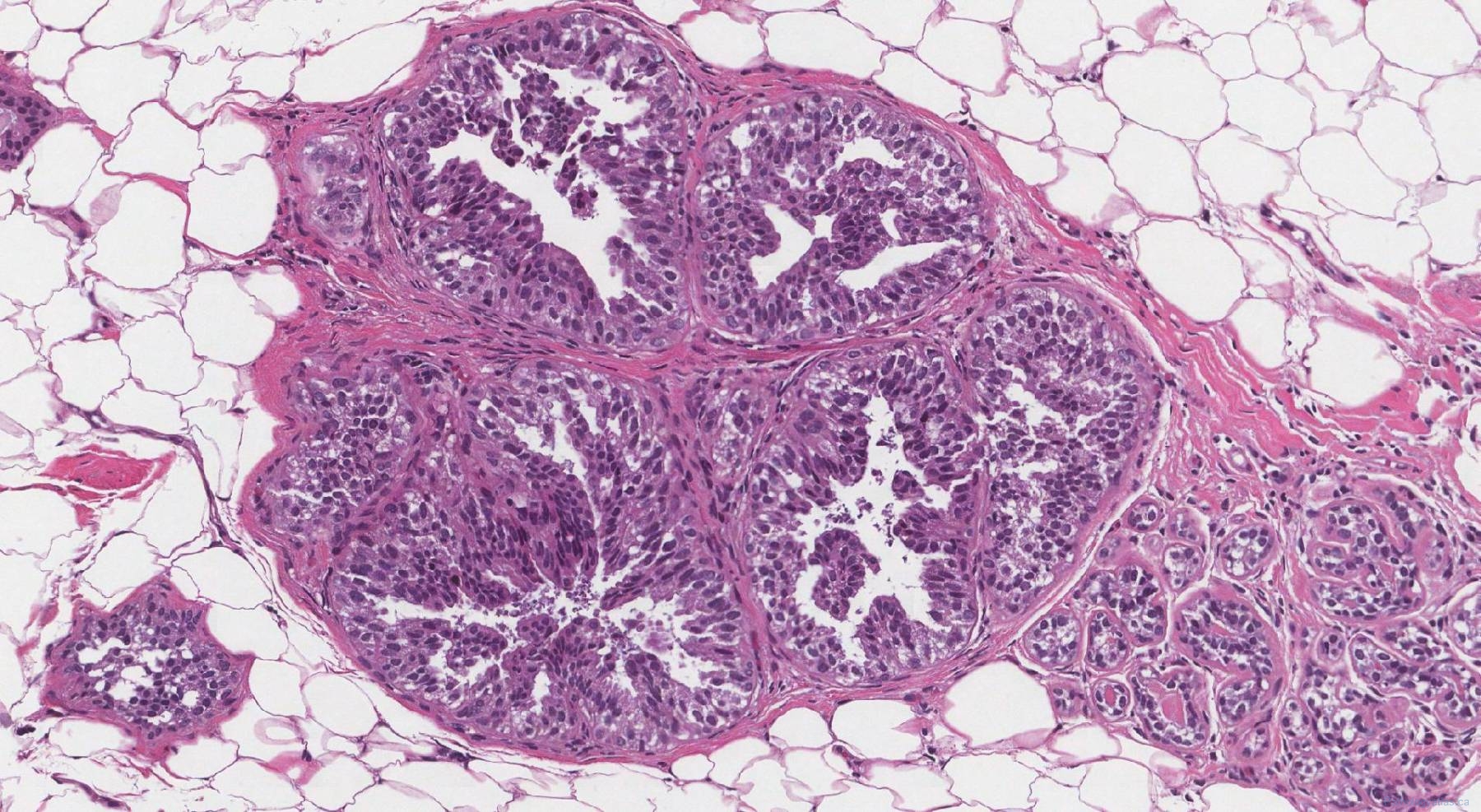
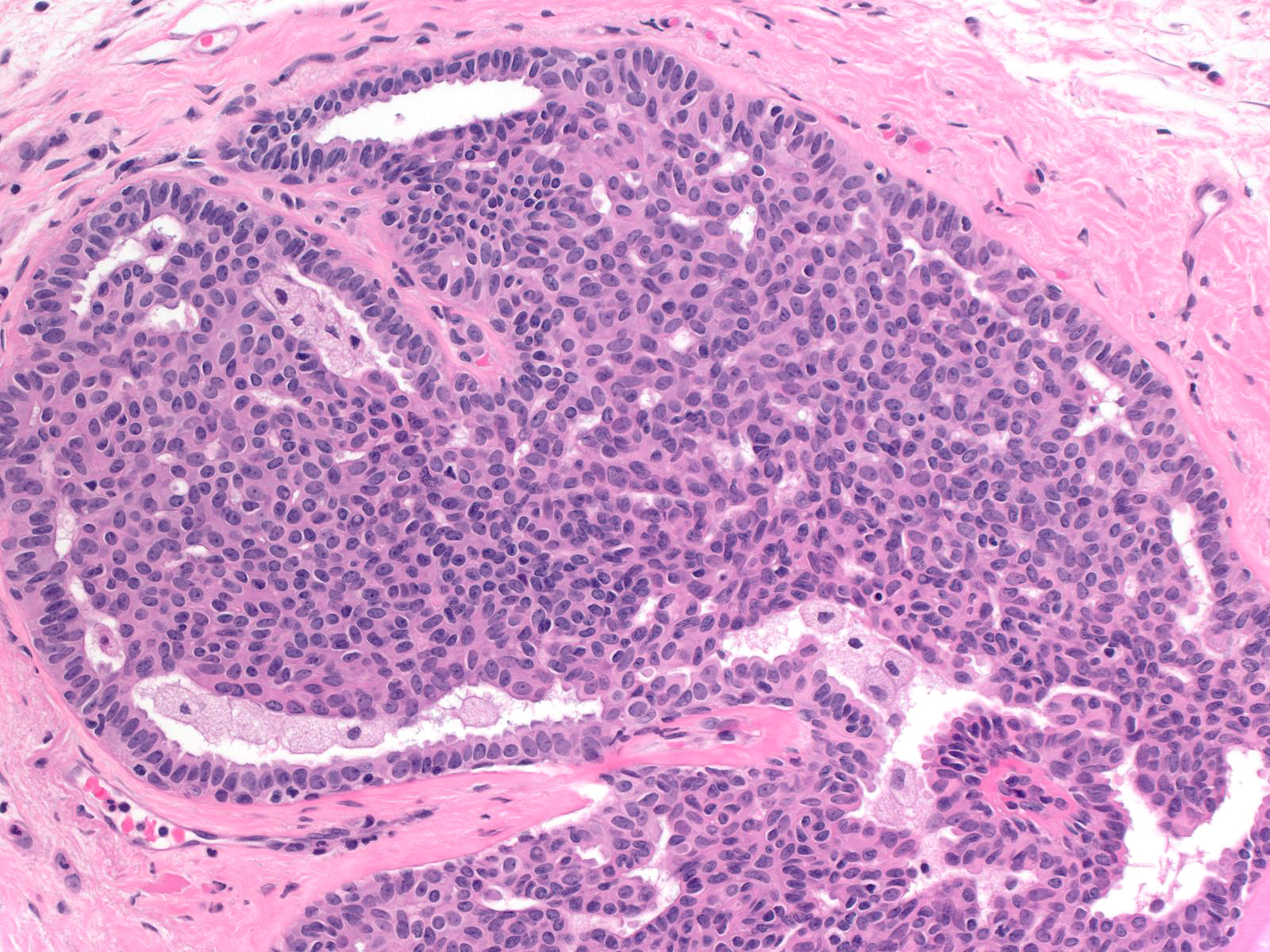
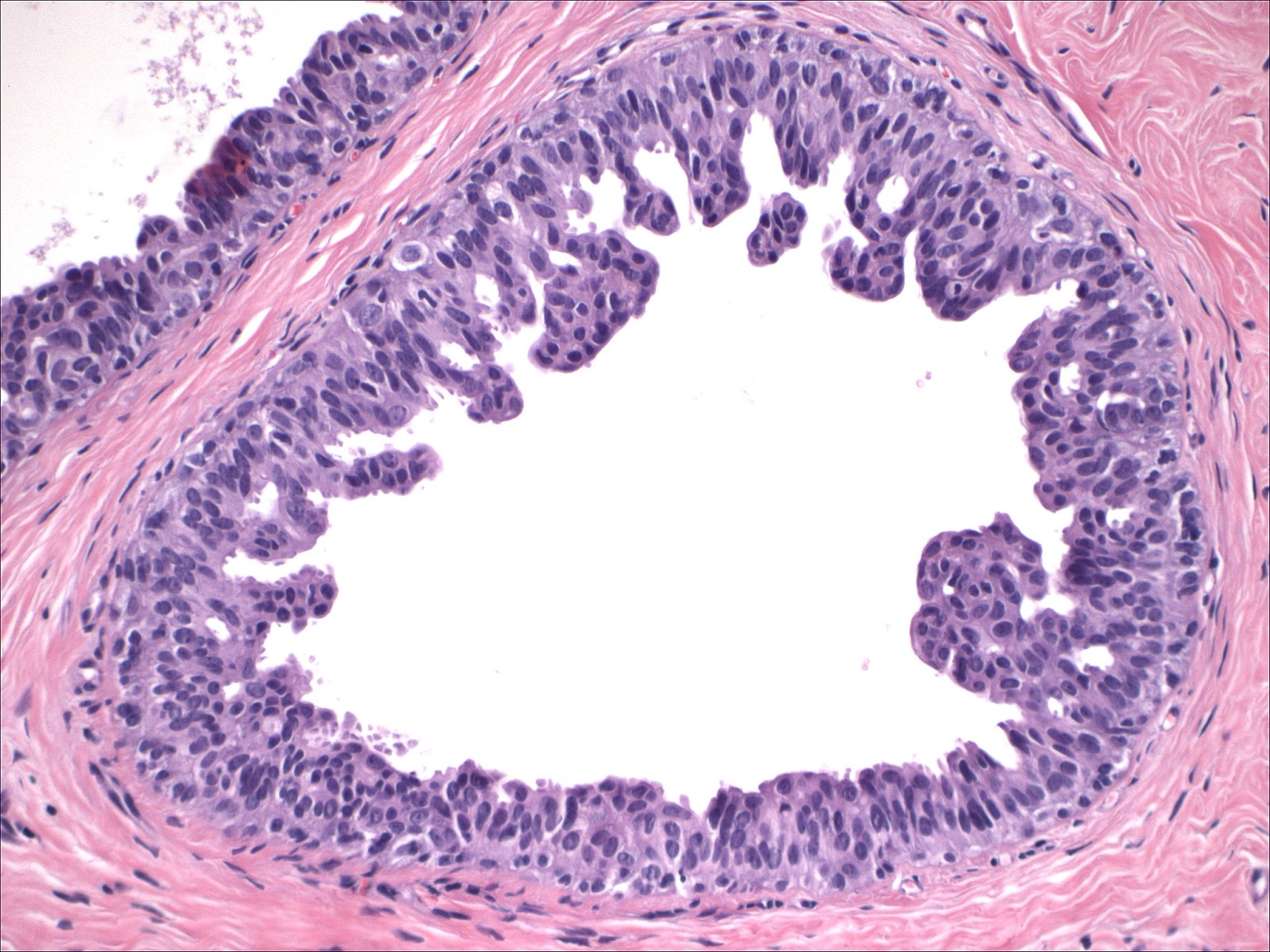
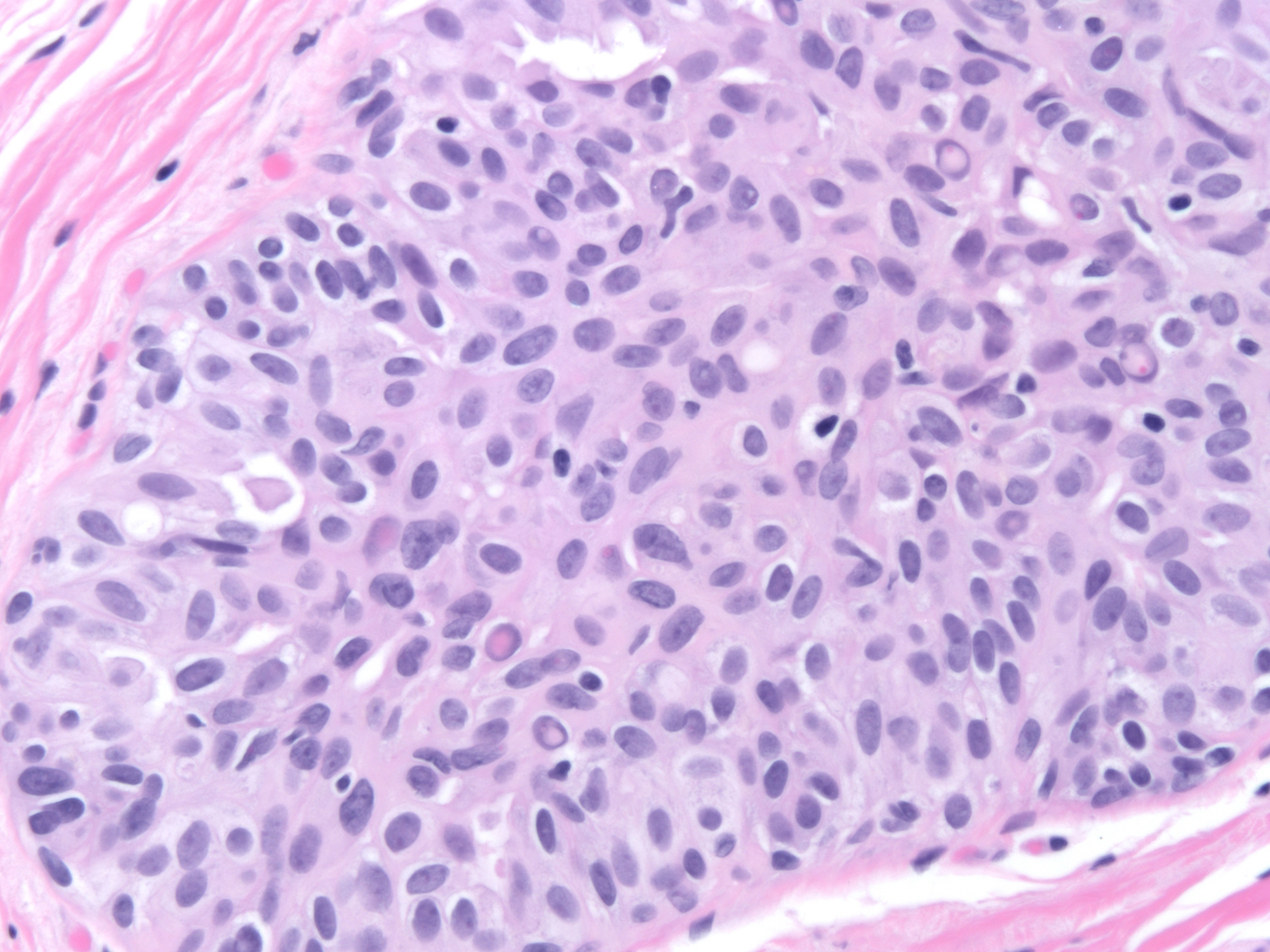
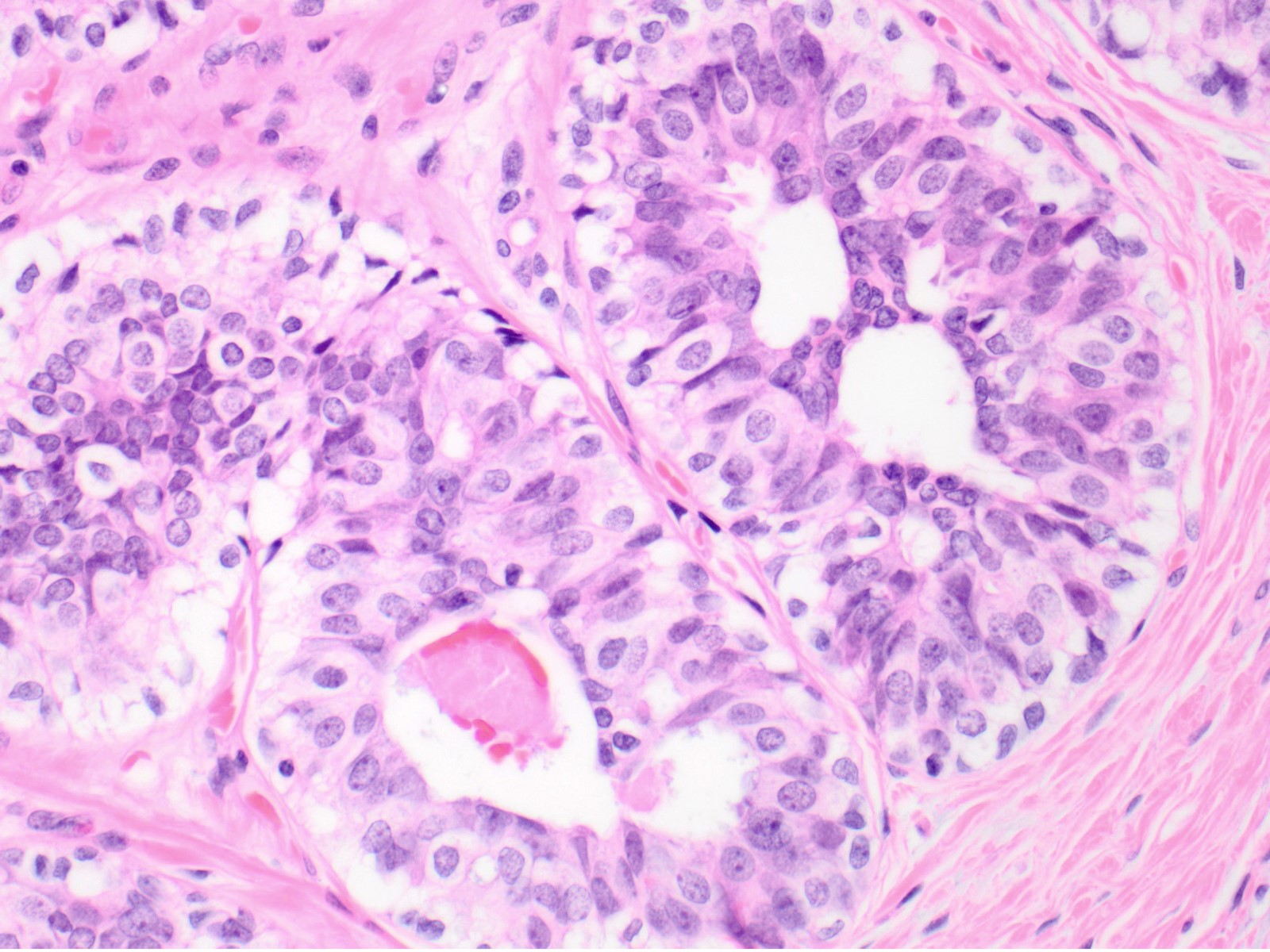
Usual Ductal Hyperplasia
Usual Ductal Hyperplasia - There are 2 types of hyperplasia: With usual hyperplasia, the dividing cells look normal under a microscope. Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. The risk of breast cancer is about 1½ to 2 times higher than that of a woman with no. Usual hyperplasia (more common) and atypical hyperplasia (less common). Usual ductal hyperplasia (also known as moderate or florid hyperplasia of the usual type, without atypia): There are 2 types of hyperplasia: In usual hyperplasia (the most common form of hyperplasia), the. With atypical hyperplasia, the dividing cells.
There are 2 types of hyperplasia: With atypical hyperplasia, the dividing cells. In usual hyperplasia (the most common form of hyperplasia), the. Usual hyperplasia (more common) and atypical hyperplasia (less common). The risk of breast cancer is about 1½ to 2 times higher than that of a woman with no. Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. There are 2 types of hyperplasia: Usual ductal hyperplasia (also known as moderate or florid hyperplasia of the usual type, without atypia): With usual hyperplasia, the dividing cells look normal under a microscope.
With usual hyperplasia, the dividing cells look normal under a microscope. With atypical hyperplasia, the dividing cells. The risk of breast cancer is about 1½ to 2 times higher than that of a woman with no. There are 2 types of hyperplasia: In usual hyperplasia (the most common form of hyperplasia), the. Usual hyperplasia (more common) and atypical hyperplasia (less common). Usual ductal hyperplasia (also known as moderate or florid hyperplasia of the usual type, without atypia): Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. There are 2 types of hyperplasia:
Ductal Carcinoma Breast Detailed Medical Illustration Beginning Normal
With usual hyperplasia, the dividing cells look normal under a microscope. Usual ductal hyperplasia (also known as moderate or florid hyperplasia of the usual type, without atypia): There are 2 types of hyperplasia: There are 2 types of hyperplasia: The risk of breast cancer is about 1½ to 2 times higher than that of a woman with no.
Pathology Outlines Usual ductal hyperplasia
The risk of breast cancer is about 1½ to 2 times higher than that of a woman with no. There are 2 types of hyperplasia: In usual hyperplasia (the most common form of hyperplasia), the. Usual hyperplasia (more common) and atypical hyperplasia (less common). Usual ductal hyperplasia (also known as moderate or florid hyperplasia of the usual type, without atypia):
Usual ductal hyperplasia of the breast Ottawa Atlas of Pathology
Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. There are 2 types of hyperplasia: The risk of breast cancer is about 1½ to 2 times higher than that of a woman with no. With atypical hyperplasia, the dividing cells. Usual ductal hyperplasia (also known as moderate or florid hyperplasia of the usual type, without atypia):
Usual Ductal Hyperplasia of Breast
There are 2 types of hyperplasia: With usual hyperplasia, the dividing cells look normal under a microscope. Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. There are 2 types of hyperplasia: Usual hyperplasia (more common) and atypical hyperplasia (less common).
Pathology Outlines Usual ductal hyperplasia
There are 2 types of hyperplasia: Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. In usual hyperplasia (the most common form of hyperplasia), the. Usual hyperplasia (more common) and atypical hyperplasia (less common). The risk of breast cancer is about 1½ to 2 times higher than that of a woman with no.
Pathology Outlines Usual ductal hyperplasia
There are 2 types of hyperplasia: Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. The risk of breast cancer is about 1½ to 2 times higher than that of a woman with no. With usual hyperplasia, the dividing cells look normal under a microscope. With atypical hyperplasia, the dividing cells.
High Yield Breast Pathology Usual Ductal Hyperplasia (UDH)
There are 2 types of hyperplasia: With usual hyperplasia, the dividing cells look normal under a microscope. The risk of breast cancer is about 1½ to 2 times higher than that of a woman with no. Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. With atypical hyperplasia, the dividing cells.
Pathology Outlines Usual ductal hyperplasia
With usual hyperplasia, the dividing cells look normal under a microscope. There are 2 types of hyperplasia: Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. With atypical hyperplasia, the dividing cells. Usual ductal hyperplasia (also known as moderate or florid hyperplasia of the usual type, without atypia):
Pathology Outlines Usual ductal hyperplasia
Usual hyperplasia (more common) and atypical hyperplasia (less common). In usual hyperplasia (the most common form of hyperplasia), the. There are 2 types of hyperplasia: Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. With atypical hyperplasia, the dividing cells.
High Yield Breast Pathology Usual Ductal Hyperplasia (UDH)
With atypical hyperplasia, the dividing cells. Risk appears to be slightly higher in those patients with a positive. Usual hyperplasia (more common) and atypical hyperplasia (less common). In usual hyperplasia (the most common form of hyperplasia), the. Usual ductal hyperplasia (also known as moderate or florid hyperplasia of the usual type, without atypia):
Risk Appears To Be Slightly Higher In Those Patients With A Positive.
With atypical hyperplasia, the dividing cells. Usual hyperplasia (more common) and atypical hyperplasia (less common). The risk of breast cancer is about 1½ to 2 times higher than that of a woman with no. There are 2 types of hyperplasia:
There Are 2 Types Of Hyperplasia:
With usual hyperplasia, the dividing cells look normal under a microscope. Usual ductal hyperplasia (also known as moderate or florid hyperplasia of the usual type, without atypia): In usual hyperplasia (the most common form of hyperplasia), the.