What Distinguishes Strong Acids From Weak Acids
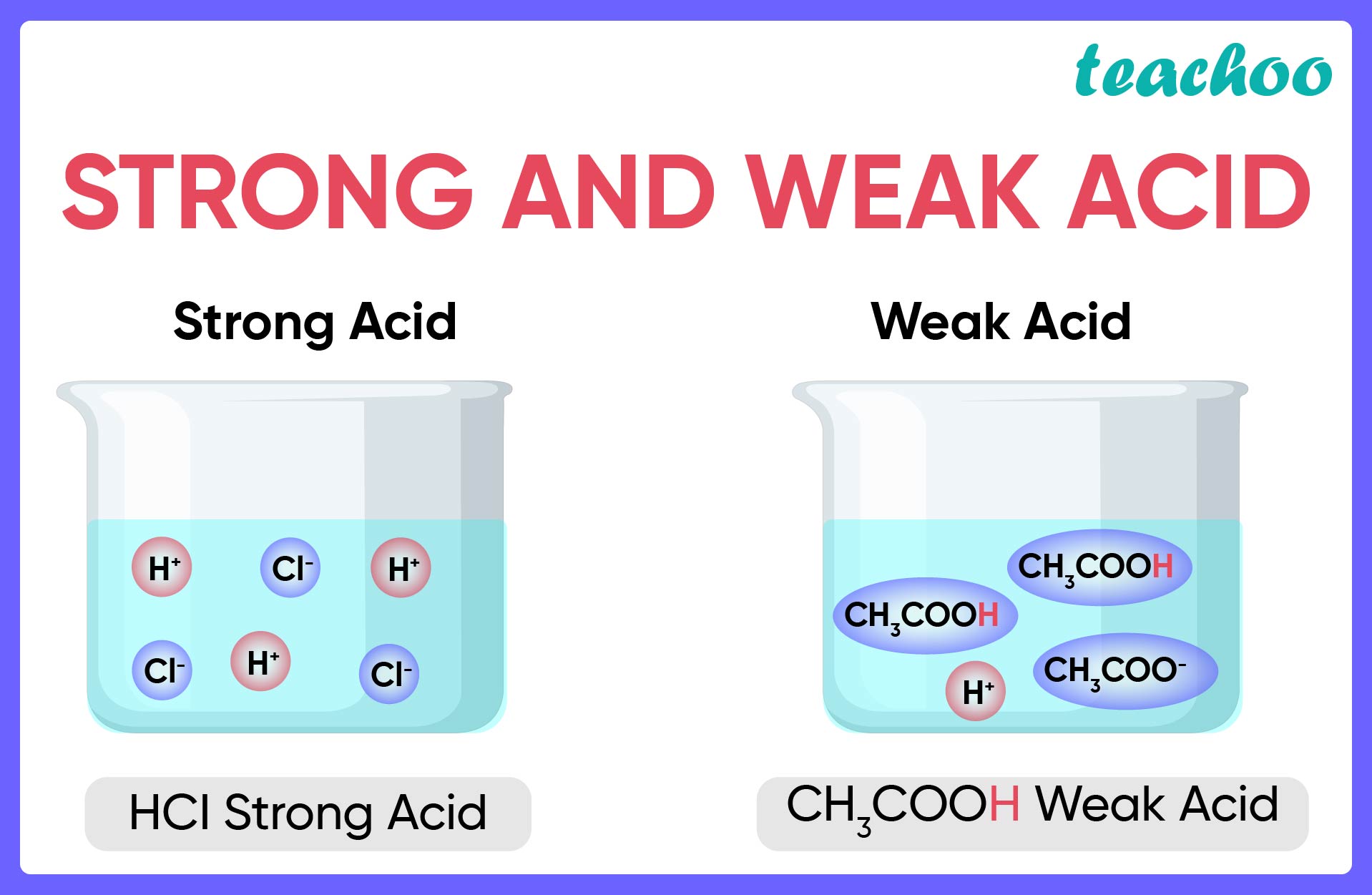
What Distinguishes Strong Acids From Weak Acids - Weak acids have a low. Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration. Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions.
Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration. Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions. Weak acids have a low.
Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration. Weak acids have a low. Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions.
Learn All About The Strong Acids and Bases PraxiLabs
Weak acids have a low. Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration. Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions.
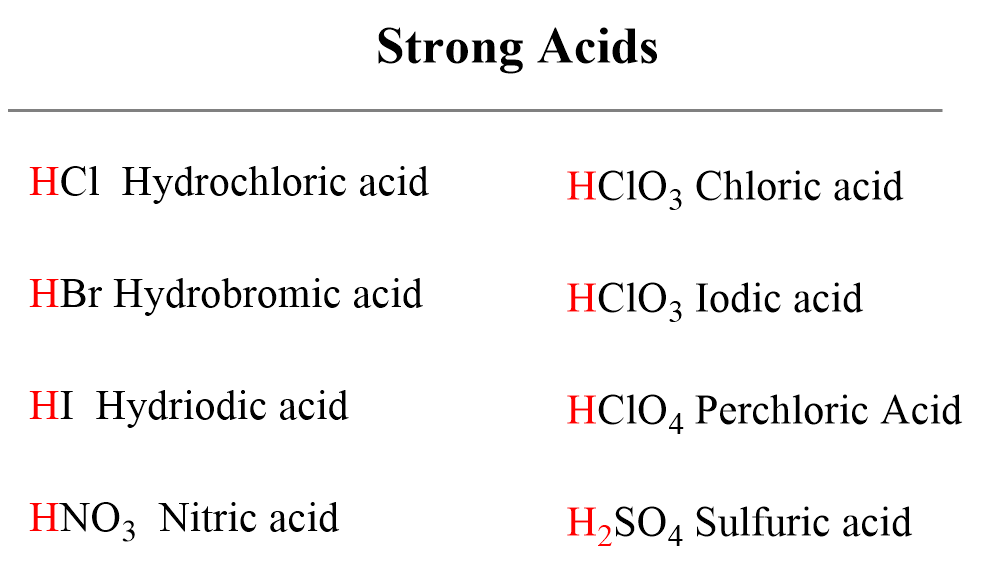
Difference between Strong and Weak Acids [in Table Form] Teachoo
Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions. Weak acids have a low. Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration.
Learning goals Students will be able to ppt download
Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions. Weak acids have a low. Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration.
Strong and weak acids collection with educational diagram outline
Weak acids have a low. Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions. Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration.
Strong Organic Acids List
Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions. Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration. Weak acids have a low.
Strong Organic Acids List
Weak acids have a low. Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration. Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions.
Examples of Weak Acids 5+ Examples Teachoo Teachoo Questions
Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions. Weak acids have a low. Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration.
Acid Strength, Ka, and pKa Chemistry Steps
Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions. Weak acids have a low. Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration.
اسید قوی چیست و چه تفاوتی با اسید ضعیف دارد؟ شیمی یار
Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration. Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions. Weak acids have a low.
SOLVEDa. What distinguishes strong acids from weak acids? b. Give two
Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration. Weak acids have a low. Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions.
Strong Acids Usually Pass More Current As Compared To The Weak Acids For The Same Voltage And Concentration.
Strong acids are highly ionizable and completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of (h+) (h +) ions. Weak acids have a low.
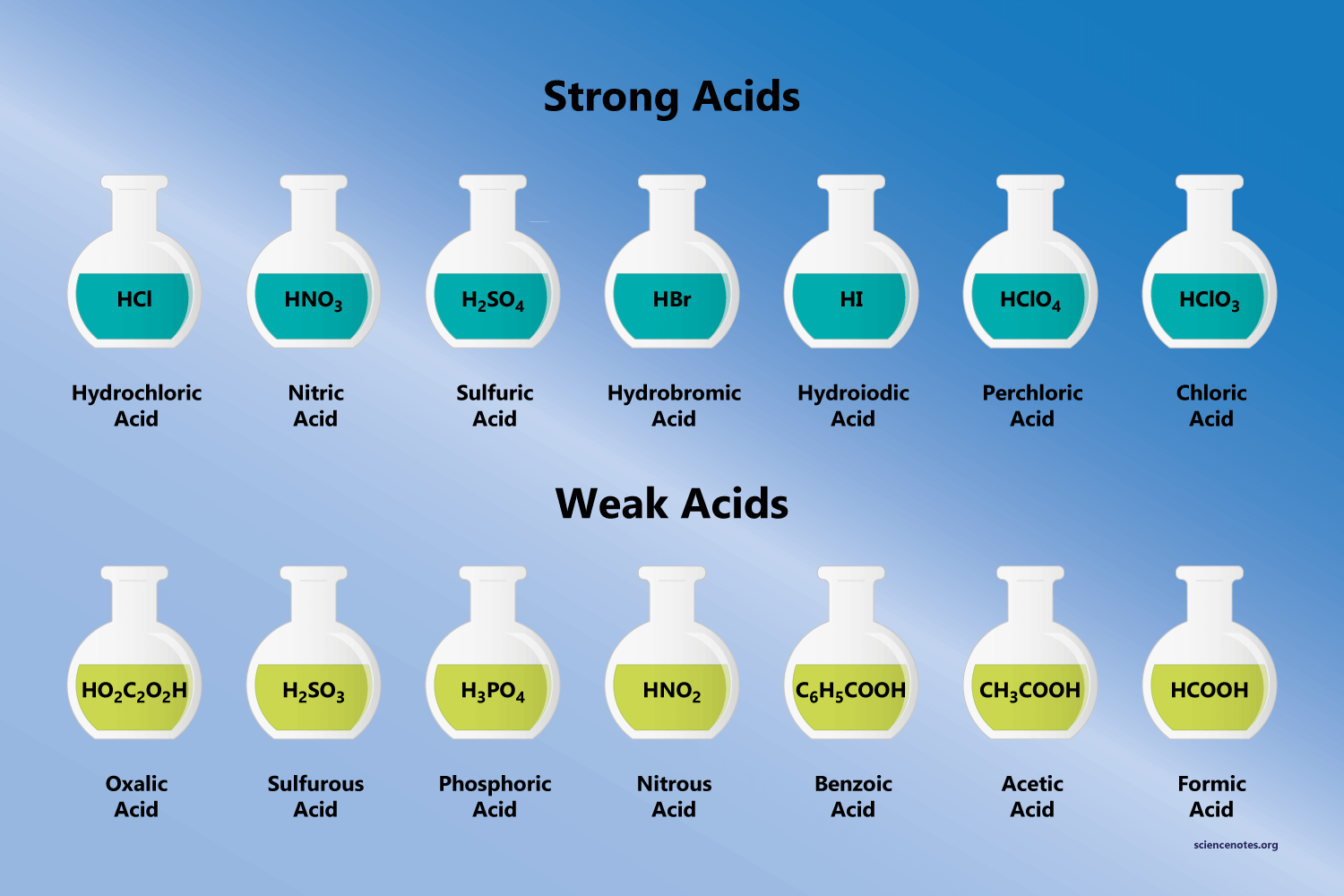
![Difference between Strong and Weak Acids [in Table Form] Teachoo](https://d77da31580fbc8944c00-52b01ccbcfe56047120eec75d9cb2cbd.ssl.cf6.rackcdn.com/eb34c57a-aeb2-4e7c-aa0b-613a11a6595e/differentiate-between-strong-and-weak-acids-01.jpg)

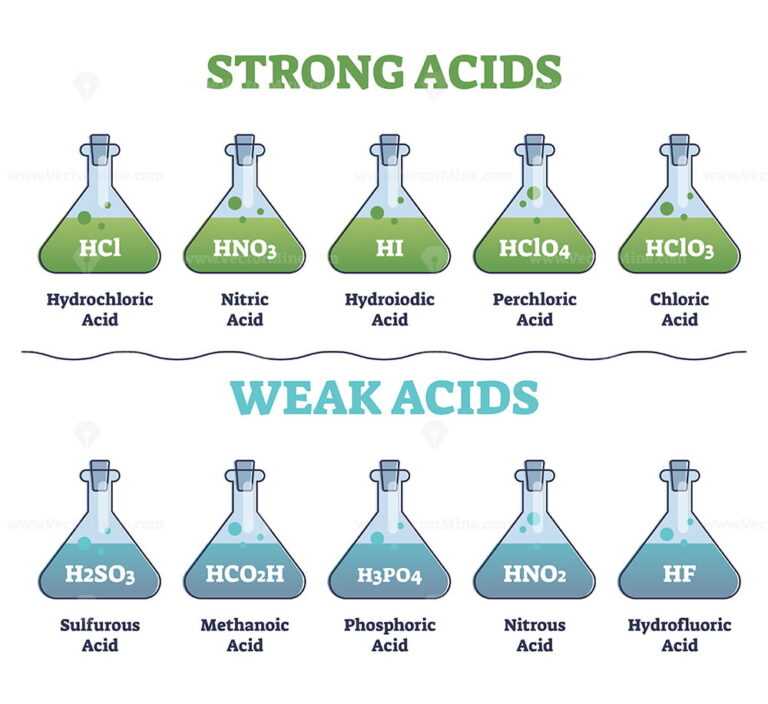
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png)