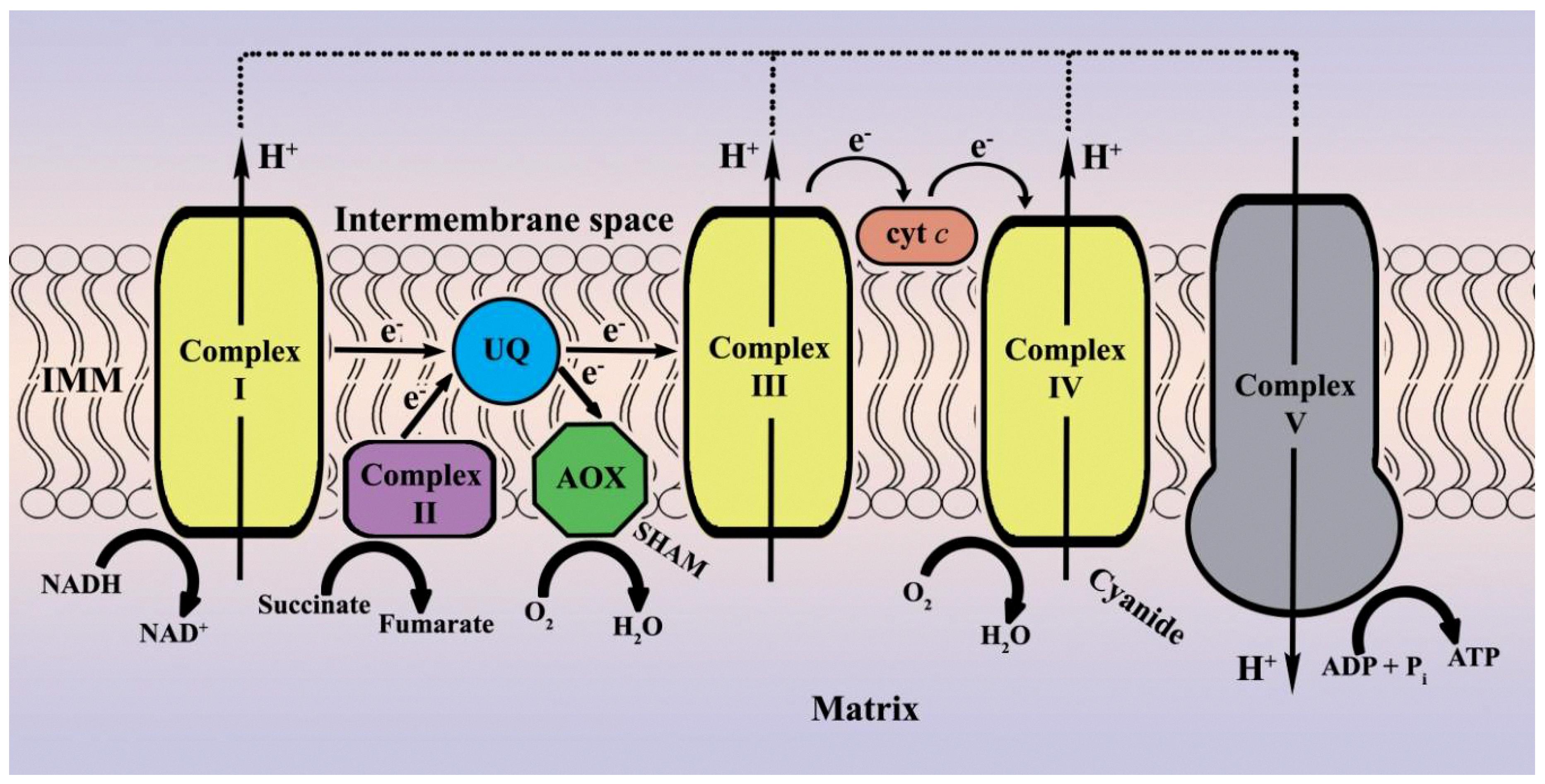
What Effect Would Cyanide Have On The Electron Transport Chain
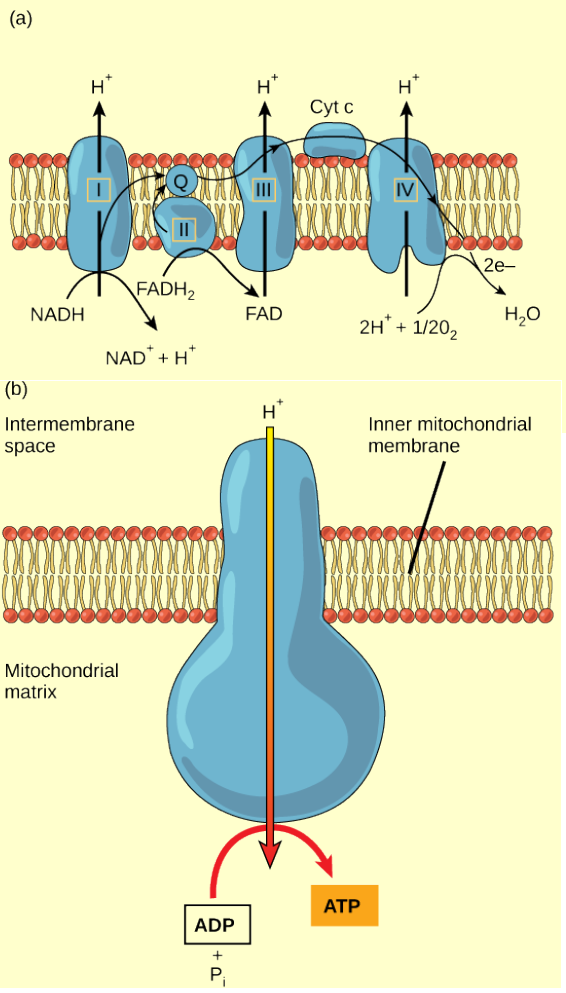
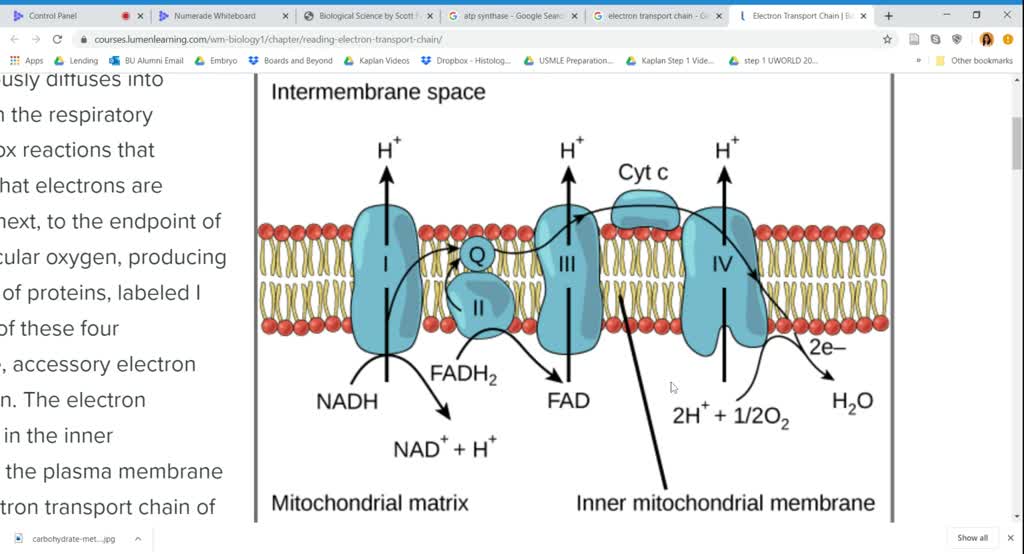
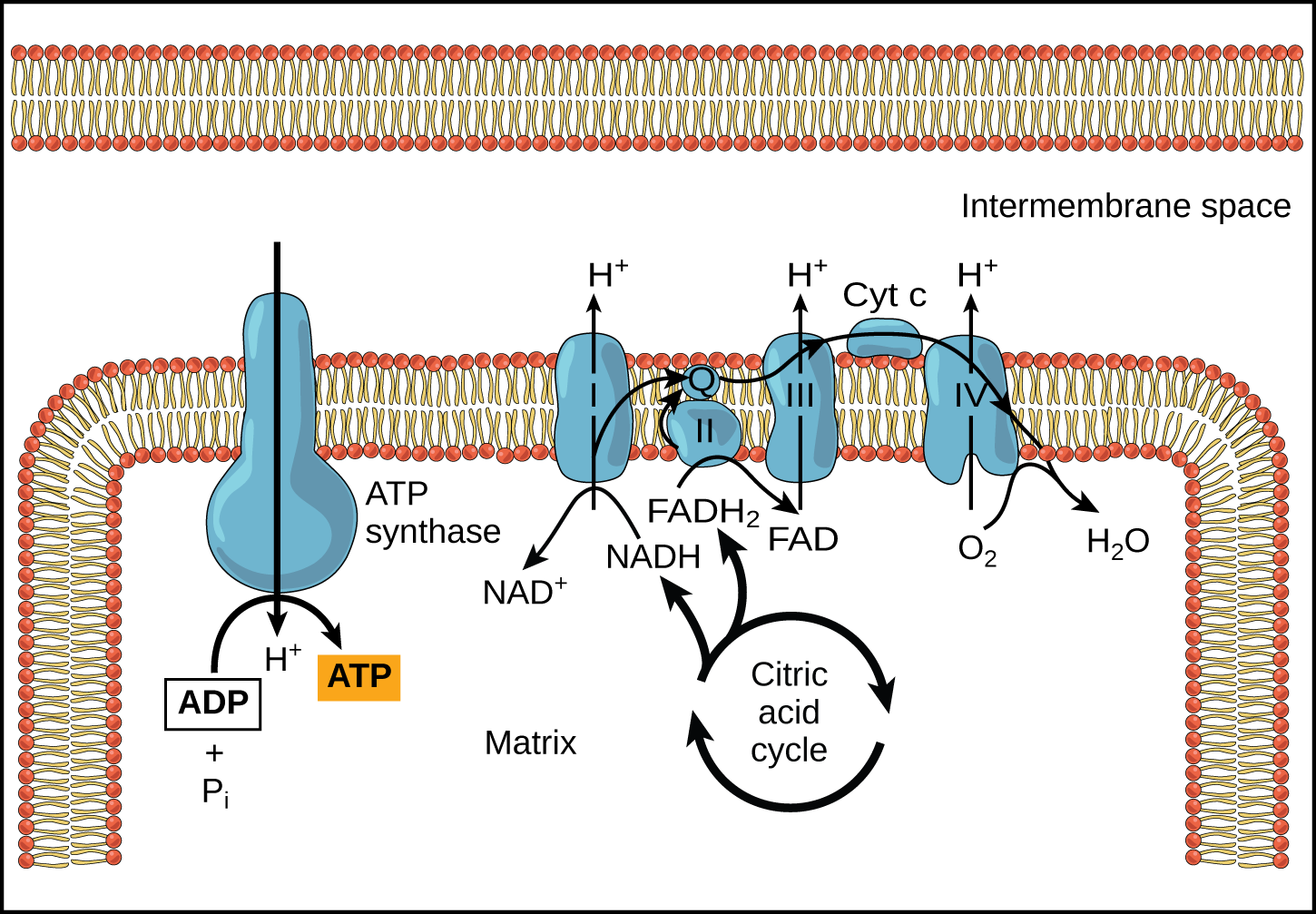
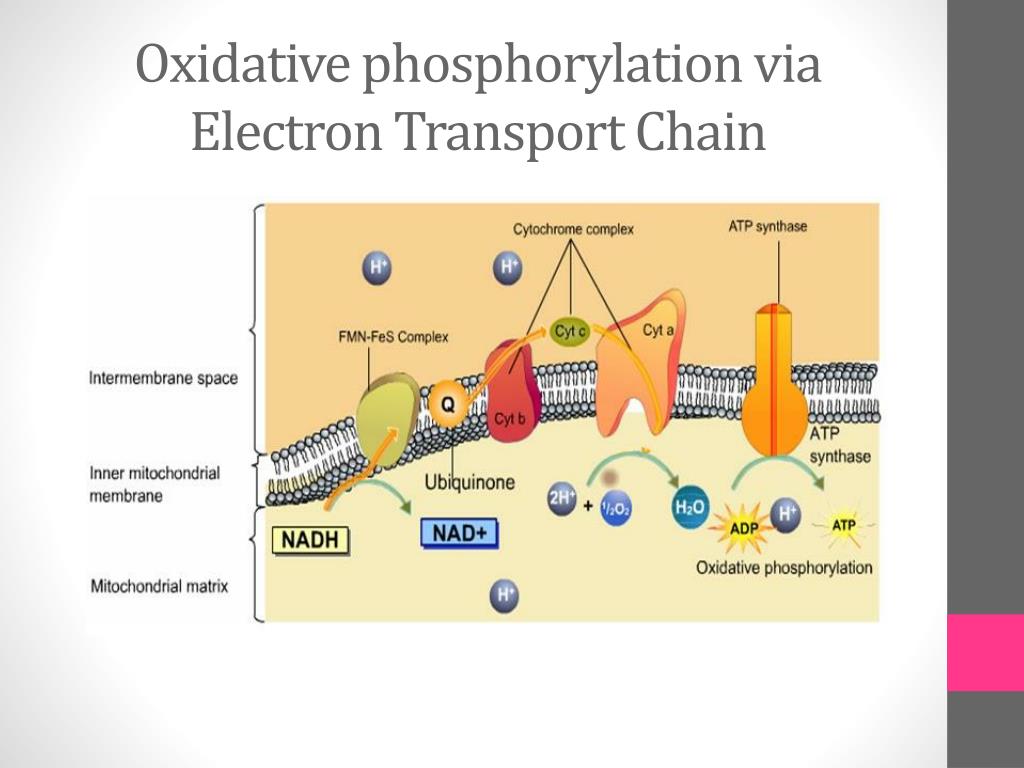
What Effect Would Cyanide Have On The Electron Transport Chain - Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain. Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain by binding to one of its components, cytochrome c oxidase (also known as complex iv). If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of the.
Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain by binding to one of its components, cytochrome c oxidase (also known as complex iv). Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain. Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of the.
Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain by binding to one of its components, cytochrome c oxidase (also known as complex iv). Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of the. Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain;
Figure 4.15 Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the
Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of the. Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain. Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; Cyanide.
Cyanide (C=N^) blocks complex IV of the electron transport chain
Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain. Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of the. Cyanide.
Emergency Medicine EducationEM3AM Cyanide Toxicity
Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of the. Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain by binding to one of its components,.
16.4 Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology 110 PSU Dubois
Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of the. Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain by binding to one of its components, cytochrome c oxidase (also known as complex.
PPT Effect of Cyanide on ATP S ynthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free
Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of the. Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. Cyanide.
As shown in Figure 7 11, cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain
Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain by binding to one of its components, cytochrome c oxidase (also known as complex iv). Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of.
SOLVED The poison cyanide prevents the last protein in the electron
Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain by binding to one of its components, cytochrome c oxidase (also known as complex iv). Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain. If.
Cyanide poisoning. No quintessentially british James bond… by Kinjal
Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain. Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of the. Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; Cyanide.
Electron Transport Chain Steps
Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of the. Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain by binding to one of its components, cytochrome c oxidase (also known as complex iv). Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport.
Cyanide's Effects on Cellular Respiration
Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain by binding to one of its components, cytochrome c oxidase (also known as complex iv). Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain. Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; If cyanide poisoning occurs, would the ph of.
If Cyanide Poisoning Occurs, Would The Ph Of The.
Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain by binding to one of its components, cytochrome c oxidase (also known as complex iv). Cyanide inhibits cyochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain; Cyanide disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria by binding to cytochrome oxidase, preventing the mitochondria from using oxygen. Once it is reduced, (qh 2), ubiquinone delivers its electrons to the next complex in the electron transport chain.