Which Amino Acid Can Form Disulfide Bonds
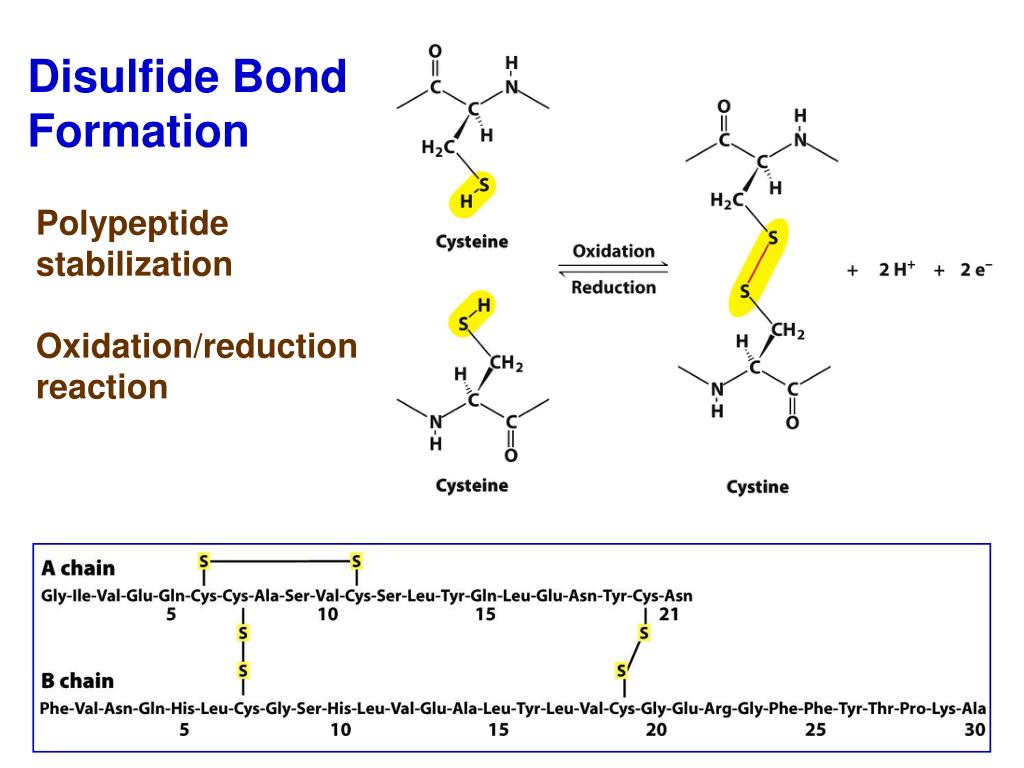
Which Amino Acid Can Form Disulfide Bonds - Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them.
Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein.
Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them. Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein.
PPT Proteins Amino Acid Chains PowerPoint Presentation, free
Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive.
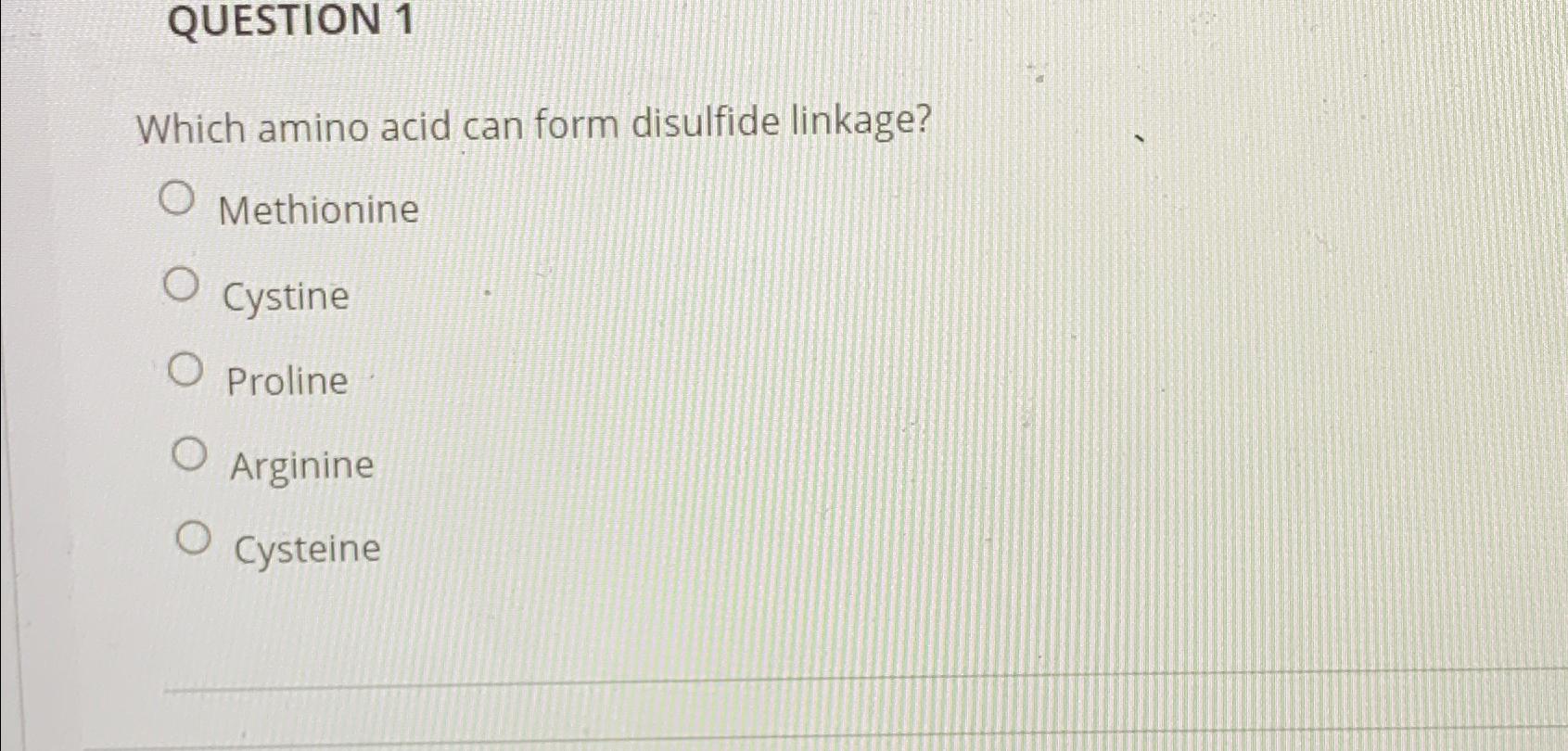
Solved QUESTION 1Which amino acid can form disulfide
Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge.
What amino acid forms disulfide bonds to stabilize protein t Quizlet
The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive.
Biochemistry Glossary Amino Acid Modifications Draw It to Know It
The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive.
Amino acids and the disulfide bond are related to antioxidant activity
Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive. Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them.
A piece of a sequence of amino acids, with two disulfide bonds between
Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein.
Structure of Amino Acids and Proteins
The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them.
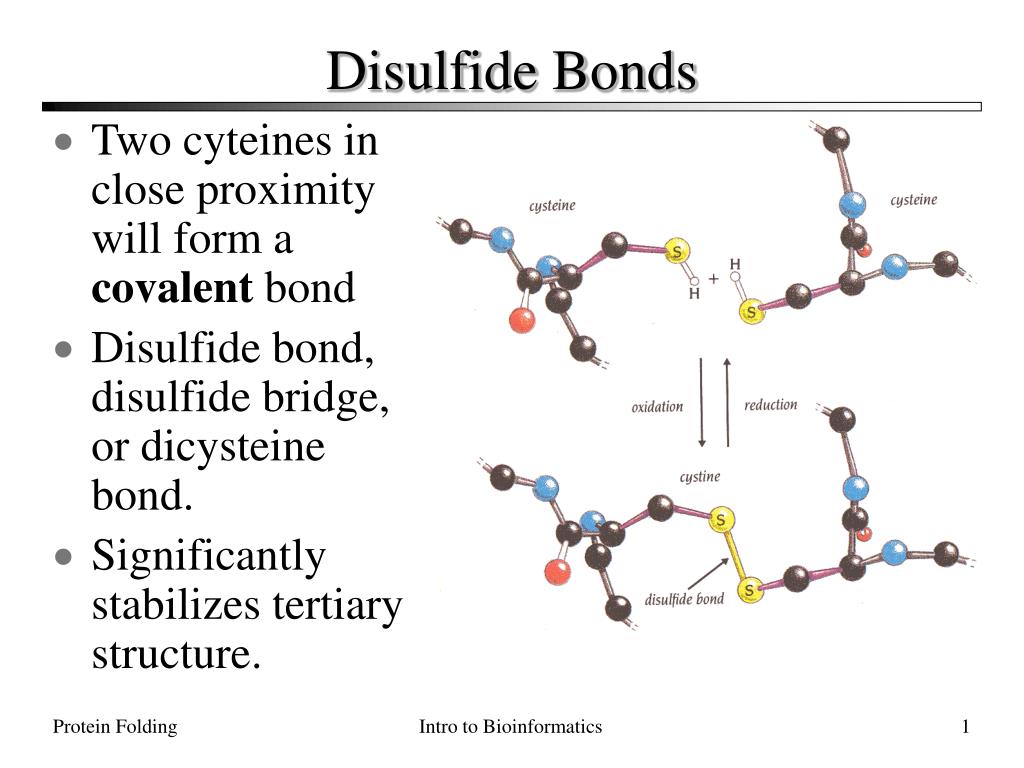
PPT Disulfide Bonds PowerPoint Presentation ID165240
Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive.
IJMS Free FullText Amino Acid Patterns around Disulfide Bonds
Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein.
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas intracellular proteins usually lack them.
Extracellular Proteins Often Have Several Disulfide Bonds, Whereas Intracellular Proteins Usually Lack Them.
Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues in a protein. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a highly reactive. The covalent bond formed between the thiol groups from two cysteine amino acids is called a disulfide bond or a disulfide bridge.