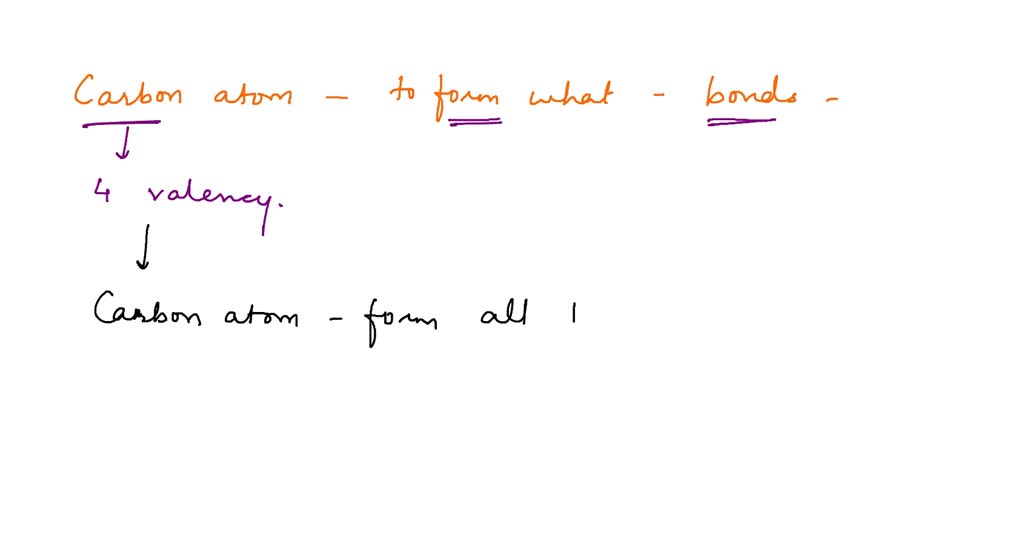Which Atoms Are Most Likely To Form Covalent Bonds
Which Atoms Are Most Likely To Form Covalent Bonds - The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming. Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms.
For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule.
The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms.
Which diagram shows how the covalent bonds most likely form in a
Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming.
__TOP__ How Many Covalent Bonds Can Chlorine Form
For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming. Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule.
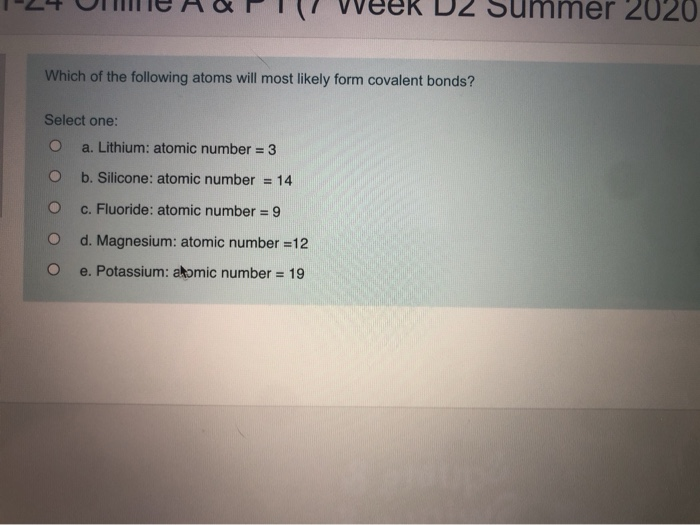
Solved mmer 2020 Which of the following atoms will most
Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming.
Covalent Bonding (Biology) — Definition & Role Expii
For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming.
Covalent Bond Definition and Examples
Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming.
which of the following pairs of atoms would be most likely to form a
Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming.
which compound is most likely to be held together by a covalent bond
Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule.
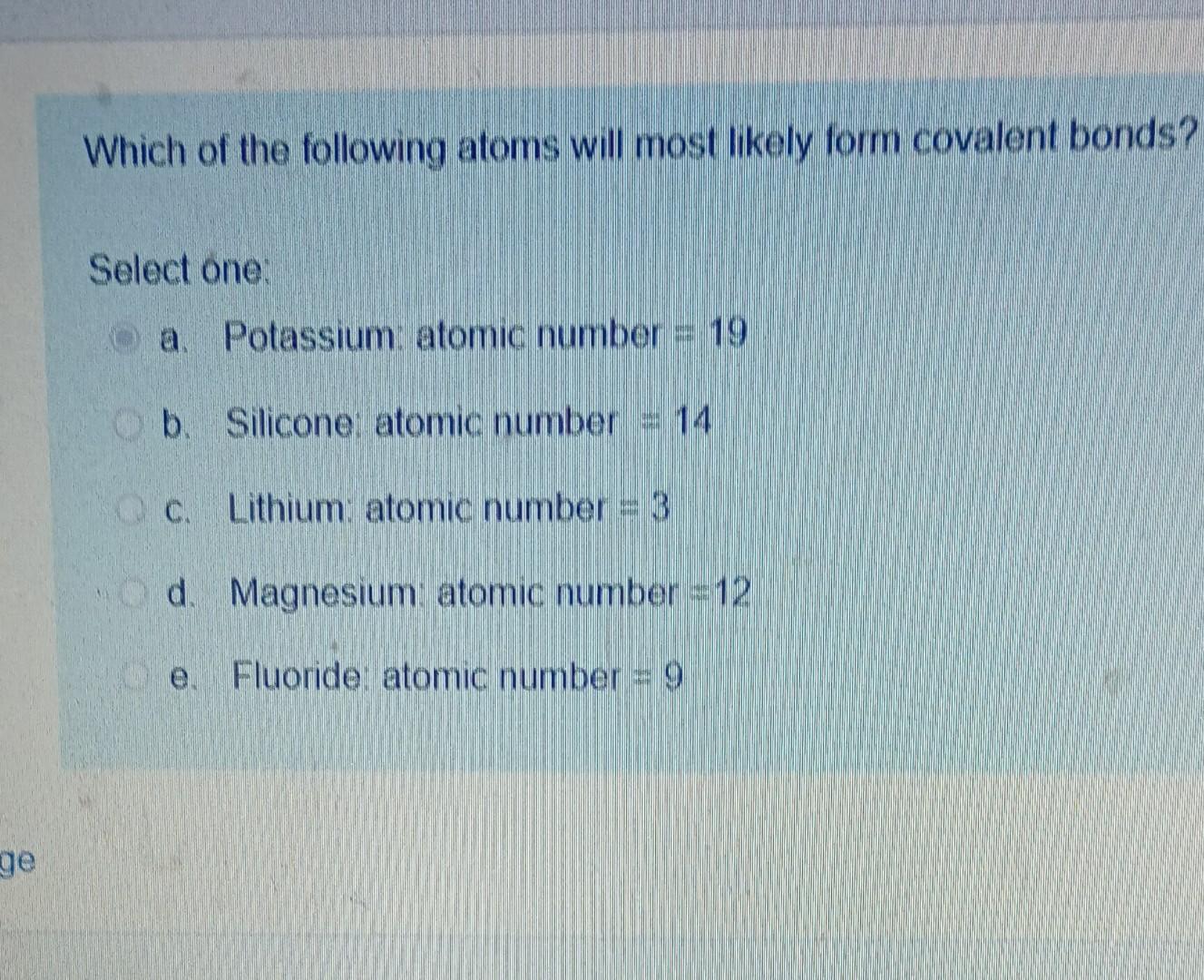
Which of the following atoms will most likely form
Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule. The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms.
What Best Describes a Covalent Bond KenziehasNicholson
Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent candidate for forming. The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,.
SOLVED A carbon atom is most likely to form what kind of bond(s) with
Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds to satisfy the octet rule. The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. Hydrogen is highly electronegative and has a small atomic radius, making it an excellent.
Hydrogen Is Highly Electronegative And Has A Small Atomic Radius, Making It An Excellent Candidate For Forming.
For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2,. The periodic table and trends in valence electrons can be used to determine the. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms.